There has never been more data in the world. As businesses become increasingly digital, they can easily collect information on processes, customer behaviours, product performance and more. This is a phenomenon known as big data, referring to the vast and varied datasets generated across digital touchpoints, operations and customer interactions.
But while many businesses are data rich, most are also insight poor. Instead of using data to drive better decision-making, businesses are often overwhelmed by the volume and struggle to make sense of it.
The challenge is no longer collecting data but using it appropriately to drive powerful outcomes. This means transforming raw data into strategic value in your business.
This blog explores how to navigate the big data landscape, uncover actionable insights and leverage the right technologies to drive smarter decisions.
Sources of big data
In the era of big data, where does your business information tend to come from? By understanding the sources of your data, it becomes much easier to build a strategy to derive meaning from it. Here are some common areas of business data:
1. Customer-generated data
This is one of the richest and most dynamic sources of big data. It reflects how customers engage with your brand across digital and physical touchpoints, offering direct insight into preferences, behaviours and sentiment.
- Websites and apps: Clickstreams, page views, time spent and navigation paths reveal how users interact with your digital platforms.
- Social media: Posts, likes, shares, comments and sentiment analysis help gauge brand perception and trending topics.
- Surveys and feedback forms: Structured responses and open-ended feedback provide qualitative and quantitative insights into customer satisfaction.
- Customer support interactions: Chat logs, call transcripts and email exchanges uncover recurring issues and service quality trends.
2. Transactional data
Transactional data forms the backbone of operational analytics. It captures the financial and behavioural footprint of customer and business activities.
- Point-of-sale systems: Record purchases, returns and payment methods, helping track sales performance and customer preferences.
- E-commerce platforms: Monitor cart activity, product views and checkout behaviour to optimise conversion strategies.
- Banking and financial systems: Include invoices, payments and account activity, supporting financial forecasting and compliance.
3. Machine-generated data
As businesses adopt more connected technologies, machine-generated data becomes a vital source for automation, predictive analytics and operational efficiency.
- IoT devices and sensors: Provide real-time data on temperature, motion, location and usage.
- Industrial equipment: Logs maintenance events and performance metrics, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Smart devices: Wearables, smart home systems, and connected vehicles generate behavioural and environmental data that can be used for product development and user experience enhancements.
4. Enterprise systems
Internal business platforms are treasure troves of structured data. They support everything from customer engagement to supply chain management.
- CRM systems: Store customer profiles, engagement history and sales pipelines, enabling personalised marketing and service.
- ERP systems: Manage inventory, HR, finance and supply chain data, supporting operational planning and resource allocation.
- Marketing automation tools: Track campaign performance, lead scoring and conversion metrics to refine outreach strategies.
5. Public and third-party data
External data sources add valuable context to internal datasets, helping businesses benchmark performance and anticipate market shifts.
- Open government data: Includes census data, economic indicators and weather patterns, useful for demographic analysis and forecasting.
- Market research firms: Provide insights into consumer trends, competitive landscapes and industry benchmarks.
- Social listening tools: Aggregate sentiment and brand mentions across platforms, helping monitor reputation and emerging issues.
6. Communication channels
Every interaction within and outside the organisation can be mined for insight. Communication data helps assess engagement, collaboration and productivity.
- Email and messaging platforms: Analyse engagement rates and content to improve communication strategies.
- Video conferencing tools: Meeting transcripts and participation metrics offer visibility into team dynamics and decision-making.
- Internal collaboration tools: Platforms like Slack, Teams and project management systems capture workflows and employee interactions.
7. Multimedia content
Often overlooked, multimedia data is increasingly important in a visual-first digital world. AI tools are essential for extracting value from these unstructured formats.
- Images and videos: From user-generated content to surveillance footage, these assets can be analysed for branding, security and customer engagement.
- Audio files: Call recordings, voice commands and podcasts offer rich, contextual data that supports sentiment analysis and voice-based interfaces.
This long list represents the volume of data available in the big data era. Sifting through the volume and getting a handle on the data that is key to your success is therefore crucial.
Why big data matters
As businesses increasingly collect data, turning it into insights must become a strategic priority.
When harnessed effectively, data enables leaders to make smarter decisions, faster. It provides the evidence needed to validate strategies, uncover risks and identify opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed. It shifts decision-making from reactive to proactive, helping you to stay ahead of market shifts and customer expectations.
It also plays a vital role in refining internal processes. By analysing operational data, businesses can pinpoint inefficiencies, streamline workflows and improve resource allocation. This leads to a more agile, efficient organisation.
Data also lays the foundation for innovation – supporting experimentation, rapid iteration and continuous improvement across products, services and customer experiences.
Moreover, it enables deeper understanding of customer behaviour, preferences and sentiment. With the right insights, businesses can personalise experiences, anticipate needs and deliver more relevant, timely interactions. This improves satisfaction and builds loyalty and long-term value.
But the benefits of big data come with a warning: ignoring it can be costly. Businesses that lack a clear data strategy often struggle with fragmented systems, poor data quality and missed opportunities. Decisions made without reliable data can lead to inefficiencies, reputational damage and strategic missteps. And it can cause you to quickly fall behind in competitive markets.
The big data lifecycle
Big data doesn’t just turn into insight by itself. It moves through a lifecycle that transforms raw information into meaningful action. Understanding this journey is key to building a data strategy that delivers real value.
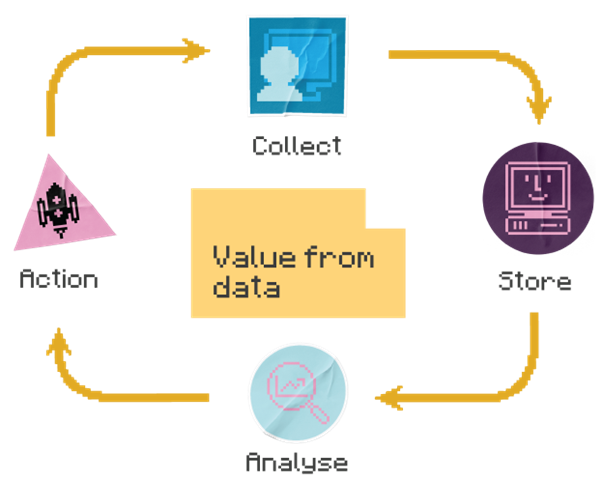
Technology underpins every stage of this lifecycle, from ingestion to insight to impact. The
right tools and platforms make it possible to manage complexity, scale efficiently and turn data into a strategic asset. Below, we dive into each stage and the types of technologies that help.
The cycle begins with collection, where data is gathered from a wide range of sources: sensors, mobile apps, transactional systems, websites and social media platforms. These inputs generate vast volumes of structured and unstructured data, often in real time. Technologies like IoT frameworks, telemetry tools and APIs enable businesses to gather real-time data at scale.
Next comes storage and management. Businesses rely on cloud platforms, data lakes and hybrid environments to store and organise their data securely and efficiently. This stage is critical for ensuring data is accessible, scalable and governed properly.
Once data is stored, it moves into the analysis phase. Here, technologies like AI, machine learning and predictive analytics come into play – identifying patterns, forecasting trends and uncovering insights that would be impossible to detect manually.
Finally, insights are translated into action. Real-time dashboards, automation tools and decision support systems help leaders respond quickly and confidently. Whether it’s adjusting a marketing campaign, optimising supply chains or improving customer service, data drives smarter outcomes.
The Microsoft technologies that make sense of your big data
With the vast sea of data likely already in your business, technology is crucial for sorting out and turning it into meaningful outcomes. This is an area Microsoft has led in for years, with several tools now available to support data collection and boost business intelligence.
Microsoft Fabric
Fabric is Microsoft’s all-in-one data platform designed to simplify and unify the entire data lifecycle. It brings together data engineering, data science, real-time analytics and business intelligence into a single environment.
What makes Fabric so valuable is its ability to eliminate the need for multiple disconnected tools. Data flows seamlessly from ingestion to insight. It’s built on a lakehouse architecture, meaning it can handle both structured and unstructured data efficiently. For businesses, this means faster access to insights, better governance and a more agile approach to analytics.
Fabric is especially powerful in the storage, management and analysis stages, acting as the backbone for scalable, secure, and collaborative data work.
Azure Synapse Analytics
Synapse is a hybrid analytics service that combines big data processing with traditional data warehousing. It allows teams to query massive datasets using either SQL or Spark, integrate with machine learning models and visualise results through built-in Power BI integration.
What’s impressive is how it handles both batch and real-time analytics, making it ideal for organisations that need flexibility and speed.
Synapse fits squarely into the analysis phase, helping businesses uncover trends, forecast outcomes and make data-driven decisions with confidence.
Power BI
Power BI is Microsoft’s business intelligence tool that turns raw data into clear, interactive dashboards and reports. It’s designed for accessibility – whether you’re a data analyst or a business leader, you can explore insights without needing to write code.
With real-time data connectivity and natural language querying, Power BI makes it easy to monitor performance, spot anomalies, and share insights across teams.
It plays a key role in the action stage of the data lifecycle, helping organisations move from insight to impact quickly and collaboratively.
Azure Data Lake and Azure Databricks
Azure Data Lake provides scalable, secure storage for all types of data: structured, semi-structured and unstructured. It’s built for high-volume workloads and integrates seamlessly with other Azure services.
Azure Databricks, meanwhile, is a collaborative analytics platform built on Apache Spark. It’s designed for data scientists and engineers to run advanced analytics, build machine learning models and process data at scale.
Together, these tools support the storage, management and deep analysis stages, making them ideal for organisations looking to build AI-driven solutions or explore complex data relationships.
Copilot in Microsoft 365 and Power Platform
Copilot brings generative AI into the tools people use every day, like Excel, Teams, Power Apps and Power Automate. It helps users ask questions of their data, summarise trends, and even build apps or automate workflows without needing technical expertise. This is a major step forward in making data accessible to everyone, not just analysts or developers.
Copilot shines in the action stage, empowering non-technical users to engage with data meaningfully and make informed decisions without barriers.
Other key tips for your big data strategy
Technology is crucial to perfecting your big data strategy, but it’s also important to have the right plans and processes in place. Here are some top tips to help you get there:
1. Align data initiatives with business goals
Start with clarity on what you want to achieve from your data.
Whether it’s improving customer retention, reducing operational costs or launching new services, your data strategy should directly support your business objectives. This ensures every data project has purpose and measurable impact.
2. Break down silos between IT and business teams
Data should be a shared resource, not confined to technical departments. Encourage collaboration between every department to ensure insights are relevant and actionable.
Cross-functional ownership leads to better outcomes and faster adoption, while ensuring everyone has equal access to data that fuels their job performance.
3. Invest in data literacy and governance
Equip teams with the skills to interpret and use data confidently. At the same time, establish strong governance frameworks to maintain data quality, security and compliance.
A well-informed workforce and trusted data foundation are essential for scaling success.
4. Start small, scale fast
Implementing a data strategy can require time and behavioural change. So, start small, focusing on high-impact, agile data projects that deliver quick wins.
Use these as proof points to build momentum and expand your capabilities. Iterative development allows you to learn quickly, adapt and grow your data maturity over time.
Unlock the power of your data
Every business has data. But being able to effectively utilise that data to drive impactful decisions and optimise performance is what will differentiate you from your competitors.
And if you are hoping to leverage AI, data is also going to be crucial for driving effective output. That’s why understanding how to make sense of your data now is key for long-term success. And we’re here to help you do exactly that.
Watch our expert-led session on data and AI, where we break down the differences between structured and unstructured data – and why both matter. Learn how AI can transform raw information into actionable insights and discover how Microsoft Fabric streamlines data management to support secure, cloud-based innovation.